Page Contents
- Program Requirements
- Concentrations
- Environmental Engineering Core Courses
- Structural Engineering Core Courses
- Transportation Systems Engineering Core Courses
- M.Eng. Project
- Project Fields
- Environmental Engineering Specializations
- Environmental and Water Resource Systems Courses
- Sustainable Energy Systems Courses
- Environmental Processes Courses
- Environmental Fluid Mechanics and Hydrology
- Structural Engineering Specializations
- Behavior and Design Track
- Advanced Materials Track
- Analysis and Computation Track
- Transportation Systems Engineering Specializations
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- City and Regional Planning
- Advisor Approved Electives
Note: This page provides a general overview. For complete and accurate information, please refer to our M.Eng. Handbook or consult the M.Eng. Student Services Coordinator. For current course offerings and information, refer to the Cornell University Registrar: Courses of Study
Program Requirements
Program core course requirements for each of the three major concentrations are provided, students round off their studies via engineering and general electives. Each student’s program is designed and approved individually in consultation with an academic advisor based on their professional aspirations.
To earn a Master of Engineering in Civil and Environmental Engineering the following requirements must be met:
- A minimum of 30 graduate-level (5000-level or above) credit hours of course and project work is required for the M.Eng. degree in Civil and Environmental Engineering.
- At maximum of 2 credits may be taken for S/U (Satisfactory/Unsatisfactory) credit in approved seminar courses
- Complete a M.Eng. Project (see more information below)
- Carry a minimum of 12 credit-bearing hours each semester
- A minimum cumulative M.Eng. GPA of 2.5
- No grade below a C-
Concentrations
-
Environmental Engineering Concentration
Our program empowers students with the expertise to drive innovation. Through a dynamic curriculum and team hands on M.Eng. project, you’ll build domain knowledge, sharpen your technical skills, and gain the analytical tools sought by employers across sectors. You’ll learn to frame complex problems, extract insight from data, and design solutions that make measurable impact.
-
Structural Engineering Concentration
Step into the forefront of structural engineering with a curriculum designed to equip you with the latest tools, technologies, and methodologies in structural behavior and design. Our program prepares engineers to create resilient, sustainable, and advanced structures that meet the demands of a rapidly evolving world. With the ability to take coursework in smart infrastructure, computational modeling, and next-generation materials individuals develop the skills and insights needed to lead in industry.
-
Transportation Systems Engineering Concentration
Join a program at the cutting edge of transportation systems engineering- where technology, data, and design converge to shape the future of mobility. Our curriculum equips engineers with advanced tools and emerging methodologies to tackle complex challenges. The program offers flexibility to tailor coursework aligned with your interests.
Environmental Engineering Core Courses
Engineering Methodology
Students should choose one from the following courses: CEE 5930 or CEE 5980 or CEE 5970
-
CEE 5930
Data Analytics (4 credits)
-
CEE 5980
Decision Framing and Analytics (3 credits)
-
CEE 5970
Risk Analysis and Management (3 credits)
Sustainable Water and Energy Applications
Students should choose two from the following courses: CEE 5420 or CEE 6210 or CEE 6530 or CEE 6560
-
CEE 5420
Energy Technologies and Subsurface Resources (3 credits)
-
CEE 6210
Renewable Energy Systems (3 credits)
-
CEE 6560
Physical and Chemical Processes (3 credits)
-
CEE 6530
Water Chemistry for Environmental Engineering (3 credits)
-
CEE 5051 or CEE 5052
Project in Environmental Engineering
-
Engineering Elective
Students must complete additional credits from 5000-level or higher courses in engineering and supporting disciplinary areas that enhance technical skills. Course selection should align with the student’s background, career goals, and academic advisor’s guidance, ensuring a well-rounded professional foundation.
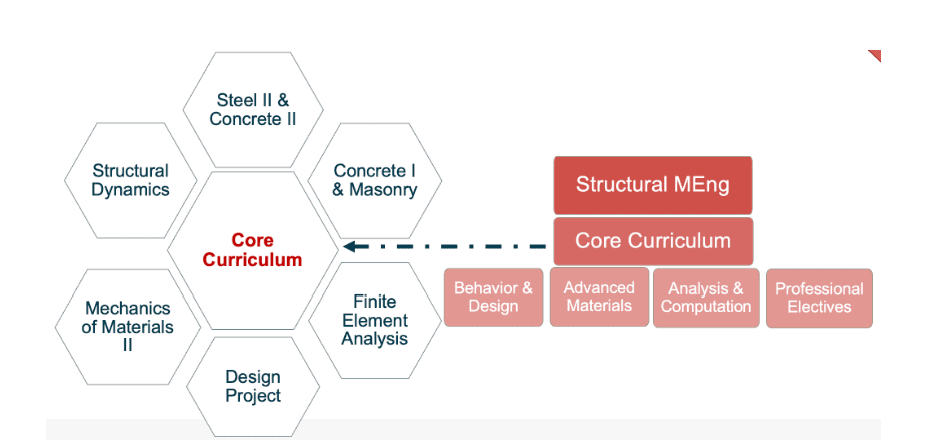
Structural Engineering Core Courses
-
CEE 5071
Professional Experience in Structural Engineering (3 credits)
-
MAE 5700
Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design (4 credits)
-
MSE 5820
Mechanical Properties of Materials, Processing, and Design (3 credits)
-
CEE 5760 (Recommended)
Behavior and Design of Concrete and Masonry Structures (4 credits)
-
CEE 6780 (Recommended)
Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering (4 credits)
-
CEE 6070 (Recommended)
CI Fall Seminar Series (.5 credits)
-
Engineering Elective
Students must complete additional credits from 5000-level or higher courses in engineering and supporting disciplinary areas that enhance technical skills. Course selection should align with the student’s background, career goals, and academic advisor’s guidance, ensuring a well-rounded professional foundation.
Transportation Systems Engineering Core Courses
-
CEE 5061 or CEE 5062
Project in Transportation Engineering (3 credits)
-
CEE 5665
Modeling and Optimization for Smart Infrastructure Systems (3 credits)
-
CEE 5930
Data Analytics (4 credits)
-
CEE 6620
Analysis and Control of Transportation Systems and Networks (3 credits)
-
CEE 6640
Microeconometrics of Discrete Choice (3 credits)
-
CEE 6648
Sustainable Transportation Systems Design (3 credits)
-
Policy course
Policy course of your choice from City and Regional Planning
M.Eng. Project
The M.Eng. program requires an engineering project of 3-6 units over 1-2 semesters. We offer a diverse selection of hands-on projects for the different majors that can either be taken over one or two semesters.
Students develop new solutions for open-ended civil and environmental engineering problems using laboratory experiments, field measurements, and/or computer modeling and simulations. Students can select projects to develop skills in engineering design, engineering research and development, and/or data analysis and decision making.
Group Projects
- Provide opportunities to apply your skills to a real engineering problem.
- Provide valuable insight to the sponsoring client
- Involve worldwide traveling for fieldwork
- Help you define a desired career path after graduation
Student teams have developed village scale sustainable water-supply treatment plant technologies and designs; seven such plants have been built in Honduras. They have modeled electricity microgrids for the waterfront energy district as well as for South Ithaca and the Cayuga Medical Center Hospital Complex, that provide energy from distributed generation in parallel with the regional grid but can also function in “island mode” during a grid failure. Work with the Ithaca Area Wastewater Treatment Facility has also extended to converting part of the waste stream into liquid fuels for use in vehicles such as trucks or public buses, and extracting energy from the heat content of the waste water itself for use in district heating. Teams have also studied local hydropower and wind resources.
Project Fields
-
Structural Engineering M.Eng. Project
Representative themes for the project experience include forensic engineering studies and failure investigations; and design of signature buildings or bridges; structural condition assessment and prognosis studies. -
Environmental Engineering M.Eng. Project
Students develop new solutions for open-ended civil and environmental engineering problems using laboratory experiments, field measurements, and/or computer modeling and simulations.
-
Interdisciplinary M.Eng. Project
The Interdisciplinary M.Eng. Projects are open to any program
-
Transportation Systems M.Eng. Project
Focuses on transportation planning, design and analysis.
Environmental Engineering Specializations
Students may mix and match among the below specializations:
- Environmental and Water Resources Systems
- Sustainable Energy Systems
- Environmental Processes
- Environmental Fluid Mechanics and Hydrology
Environmental and Water Resource Systems Courses
A student may select supporting electives from engineering and non-engineering subject areas related to environmental engineering, including biology, chemistry, toxicology, law, policy, economics, operations research, computer science, engineering mathematics, systems engineering, and city and regional planning. Add as needed to reach a total of 30 credits.
-
CEE 6790
Time Series Data Analysis for Civil, Mechanical and Geophysical Applications (3 credits)
-
CEE 5900
Project Management (4 credits)
Sustainable Energy Systems Courses
-
CEE 6648
Sustainable Transportation Systems Design (3 credits)
-
CEE 5200
Economics of the Energy Transition (3 credits)
-
CEE 6880
Applied Modeling and Simulation for Renewable Energy Systems (3 credits)
-
MAE 5020
Wind Power (4 credits)
-
MAE 5010
Future Energy Systems (3 credits)
-
CEE 6210
Renewable Energy Systems (3 credits)
-
CHEM 6660
Analysis of Sustainable Energy System (2 credits)
-
CEE 6800
Engineering Smart Cities (3 credits)
Environmental Processes Courses
-
CEE 5510
Microbiology for Environmental Engineering (3 credits)
-
CEE 6565
Wastewater Processes and Resources Recovery (3 credits)
-
CEE 6580
Biodegradation and Biocatalysis (3 credits)
-
CEE 6590
Environmental Organic Chemistry (3 credits)
Environmental Fluid Mechanics and Hydrology Courses
-
CEE 6350
Coastal Engineering (3 credits)
-
CEE 6330
Physical Hydrology in the Built and Natural Environments (3 credits)
-
CEE 6550
Transport, Mixing, and Transformation in the Environment (3 credits)
-
CEE 6790
Time Series Data Analysis for Civil, Mechanical, and Geophysical Applications (3 credits)
-
BEE 6710
Introduction to Groundwater (3 credits)
-
BEE 5730
Watershed Engineering (3 credits)
-
BEE 6790
Ecohydrology (3 credits)
Structural Engineering Specializations
Students may mix and match among the below specializations.
- Behavior and Design Track
- Advanced Materials Track
- Analysis and Computation Track
Behavior and Design Track
-
CEE 5710
Timber Behavior and Design (3 credits)
-
CEE 5790
Introduction to Building Information Modeling (BIM) using Revit (2 credits)
-
CEE 5770
Intermediate Behavior of Concrete and Metal Structures (3 credits)
-
CEE 6075
Foundation Engineering (1.5 credits)
-
CEE 6075
Tall Building Fundamentals (1.5 credits)
-
CEE 6075
Tall Building Fundamentals (1.5 credits)
-
CEE 6075
Forensic Eng & Structural Failure (1.5 credits)
Advanced Materials Track
-
CEE 5746
Sustainability and Automation: The Future of Construction Industry (4 credits)
-
ARCH 5614
Building Technology I: Materials and Methods (3 credits)
-
MSE 5820
Mechanical Properties of Materials, Processing, and Design (3 credits)
-
MAE 5670
Polymer Mechanics (3 credits)
-
MAE 6110
Foundations of Solid Mechanics (3 credits)
-
EAS 6590
Earthquake Physics (3 credits)
Analysis and Computation Track
Students may also find advisor-approved electives in the following fields:
- Engineering Management
- Architecture
- S.C. Johnson Graduate School of Management
- Real Estate
- Students are expected to take Seminar – Civil Infrastructure CEE 6070 in the fall, and CEE 6071 in the spring.
-
CEE 5745
Inverse Problems: Theory and Applications (3 credits)
-
CEE 5735
Mathematical Modeling of Natural and Engineered Systems (3 credits)
-
MAE 5770
Engineering Vibrations (3 credits)
-
CEE 6730
Finite Element Method: Theory and Applications in Mechanics and Multiphysics (3 credits)
-
CEE 6790
Time Series Data Analysis for Civil, Mechanical, and Geophysical Applications (3 credits)
-
CEE 6800
Engineering Smart Cities (3 credits)
Transportation Systems Engineering Specializations
Students may mix and match among the below specializations:
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- City and Regional Planning
Civil and Environmental Engineering
-
CEE 5900
Project Management (4 credits)
-
CEE 5970
Risk Analysis and Management (3 credits)
-
CEE 6620
Analysis and Control of Transportation Systems and Networks (3 credits)
-
CEE 6930
Public Systems Modeling (3 credits)
City and Regional Planning
-
CRP 5040
Urban Economics (3 credits)
-
CRP 5080
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for Planners (3 credits)
-
CRP 5190
Urban Theory (3 credits)
Advisor Approved Electives
-
ECON 6090
Microeconomic Theory I (3 credits)
-
ORIE 5300
Optimization I (3 credits)
-
ORIE 5310
Optimization II (3 credits)
-
ORIE 5510
Introduction to Engineering Stochastic Processes (3 credits)
-
NBA 6420
Supply Chain Analytics (1.5 credits)
Note: This is not a complete list of courses offered that can go toward degree completion. Students may take courses outside of the list as they relate to the degree with approval from their advisor.
CEE 6065 Special Topics in Transportation can be used to pursue an independent study on a particular transportation topic if you and your advisor agree that this is appropriate. In this case, the selection of appropriate core courses will depend on your background and will be determined in discussion with your advisor.